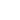
Turbine disk spline broaching
Processing difficulties of the wheel-type mortise and tenon
▲The processing precision requirements for aero-engine components are extremely stringent
1. Mortise and tenon contour accuracy: The contour accuracy of dovetail/fir-tree mortise and tenon is ≤0.015mm, and the straightness of the side wall needs to be guaranteed at 0.005mm/m
2. Positional tolerance: For 80-120 evenly distributed mortise and tenons in the circumferential direction, the cumulative error of the indexing needs to be ≤20 arc seconds
▲The special materials of the turbine disk (stainless steel, high-temperature alloy, titanium alloy, etc.) make processing difficult
1. High-temperature alloy is difficult to machine: Turbine disks commonly use Inconel 718/nickel-based alloy (tensile strength ≥1400MPa), which has a significant tendency for work hardening, and the tool is prone to diffusion wear and crater wear
2. Composite structure of different materials: Some new turbine disks use metal matrix composites (MMC), and the increased hardness accelerates tool breakage
▲High requirements for dynamic stability, anti-vibration, and burr suppression during the processing process
1. Vibration during long-overhang machining: When machining deep grooves, the ratio of the cantilever length to the diameter of the tool is ≥10:1, which is prone to causing flutter and resulting in surface waviness (Ra>0.8μm)
2. Processing heat: Continuous broaching generates an instantaneous high temperature of 400-600℃, causing local thermal expansion of the workpiece to exceed the limit
3. Burr suppression: The burr height at the edge of the mortise and tenon is ≤5μm, which has unique requirements for the design of the tool edge
Major breakthroughs in domestically produced mortise and tenon broaching equipment
Core technology independently developed: The key core technologies are independently developed and reliable, breaking through foreign technological barriers and achieving technological substitution of domestically produced equipment for the processing of turbine disk mortise and tenons in various fields such as large aircraft, fighter jets, aircraft carriers, submarines, and large hydropower stations.
Heavy-duty shock absorption technology: The particularity of turbine disk materials (stainless steel, high-temperature alloy, titanium alloy, etc.) and the requirements for the surface processing quality of the mortise and tenon make the vibration suppression requirements extremely high during the broaching process of the mortise and tenon broaching machine. We use mechanical clearance elimination structure, digital clearance elimination control, and hydraulic dynamic balancing mechanism to suppress the vibration amplitude within ±2μm.
New C-shaped cradle structure: A double-lead worm gear structure is adopted, and the clearance can be adjusted according to the actual needs of C-axis indexing; in addition, we have subverted the traditional simple hard rail structure and adopted a new guide rail combination form, which not only increases the guide rail contact area and contact rigidity, but also has better circular arc guiding and positioning accuracy, ensuring dynamic rigidity during broaching.
Φ2500mm ultra-large diameter turbine disk: Successfully developed a broaching machine capable of broaching Φ2500mm ultra-large diameter turbine disk mortise and tenons, which is also currently the largest CNC mortise and tenon broaching machine in the world.
High-speed broaching technology (40% efficiency improvement): The optimized Z-axis broaching main motion can achieve high-speed broaching at 60m/min, achieving a 40% increase in mortise and tenon broaching efficiency.
Fully automatic intelligent tool magazine: A fully automatic intelligent tool magazine that matches the intelligent process package of the broaching machine operating system can automatically replace the tool box during the broaching process according to the progress of the broaching process, without any manual intervention. This ensures the continuity of broaching, the stability of accuracy, and reduces the intensity and safety risks of manual operation.